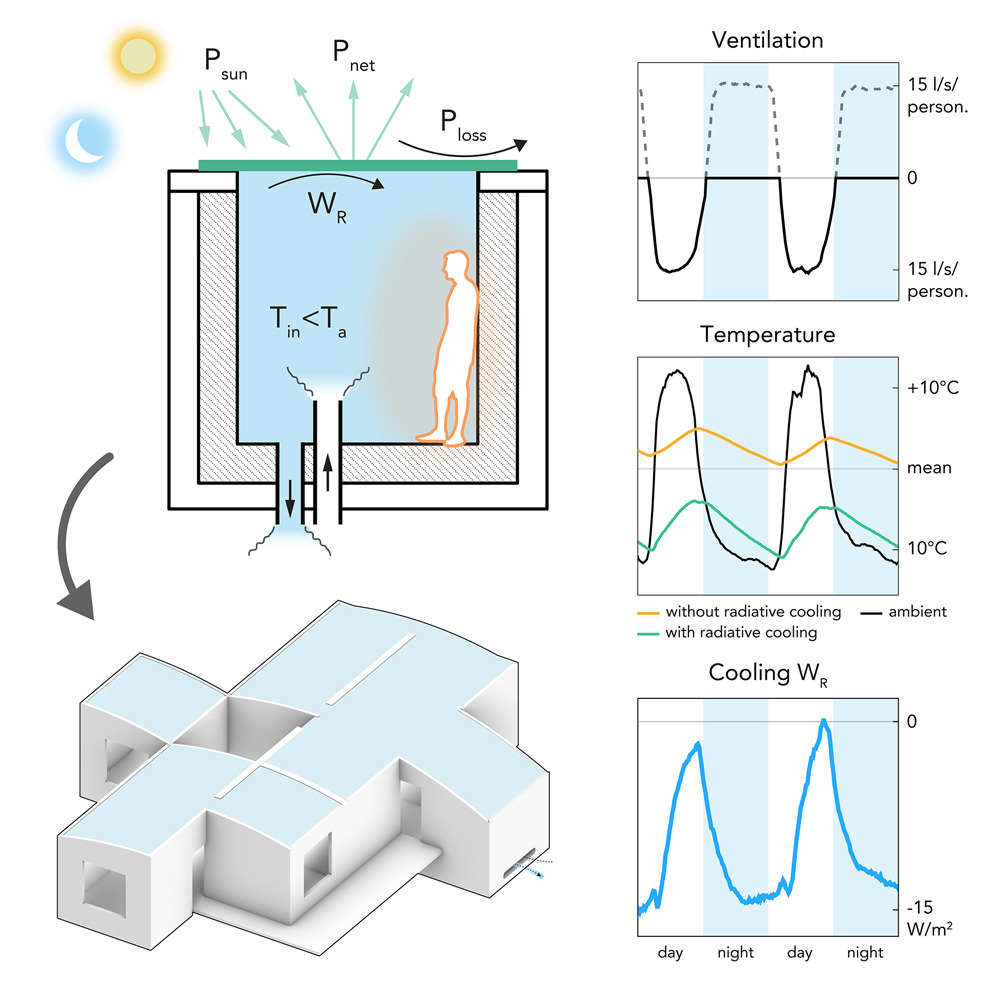
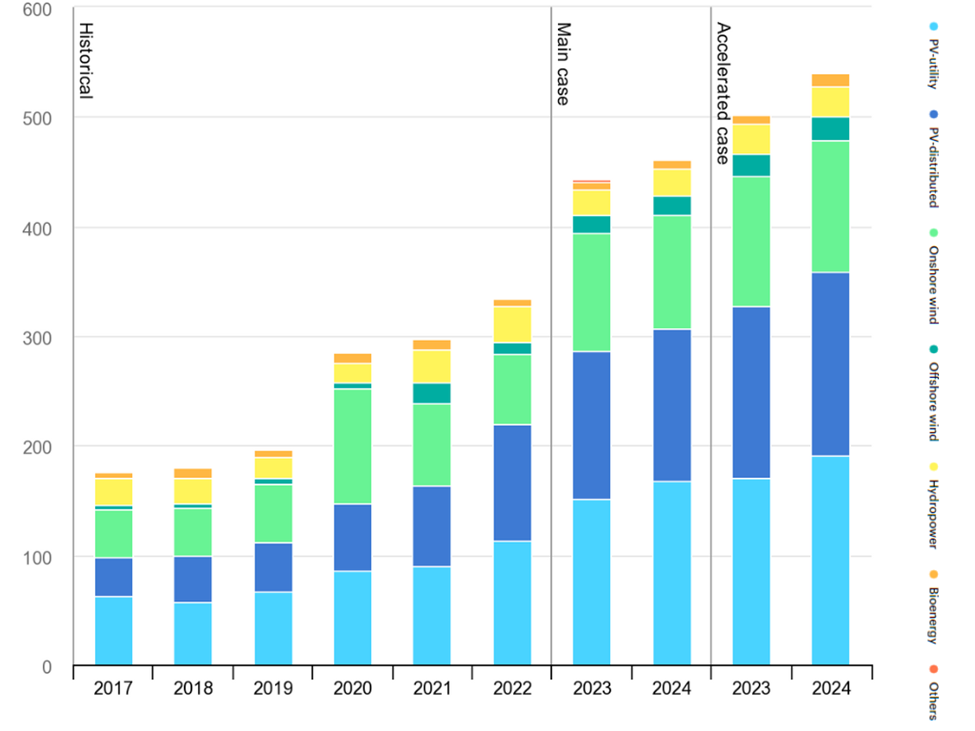
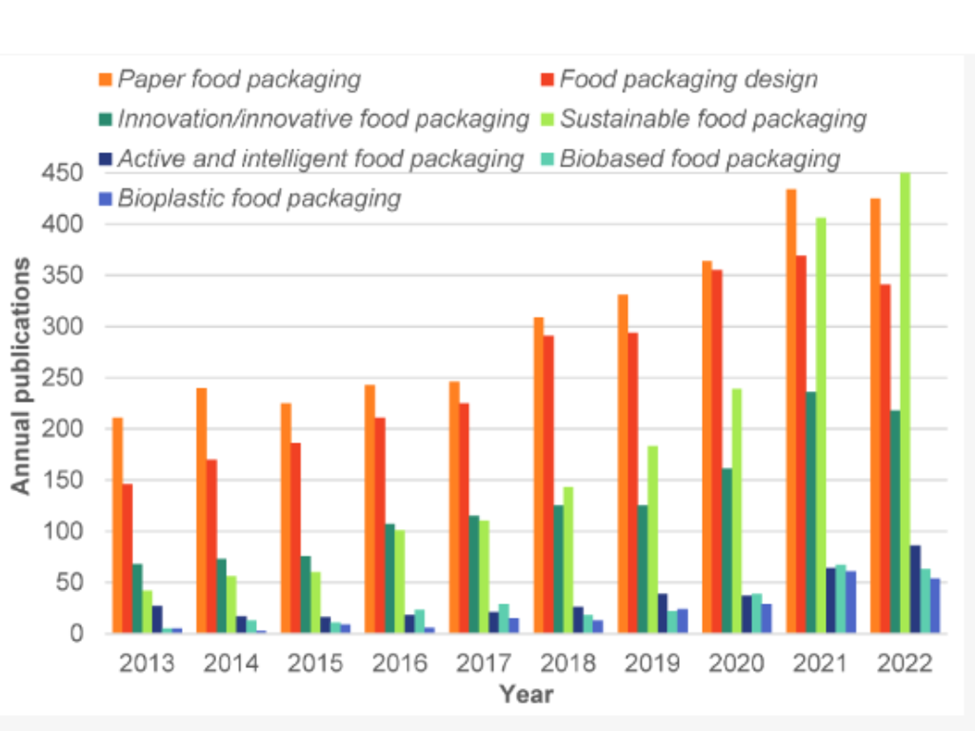
Decoding the Essence of Sustainability
Sustainability in a city is not merely a concept but a way of life meticulously woven into the urban tapestry. It’s a delicate dance between environmental stewardship, social harmony, and economic resilience. As we embark on a journey to explore the top 5 sustainable cities worldwide, let’s unravel the intricate layers that make them stand out.
The Pillars of Sustainable Cities:
1. Eco-Friendly Infrastructure:
Sustainable cities prioritize eco-friendly architecture and construction practices. Buildings are designed with energy efficiency in mind, incorporating features like green roofs, high-quality insulation, and renewable energy systems. The use of recycled and locally sourced materials further reduces the environmental impact of construction projects.
2. Efficient Public Transportation:
A hallmark of sustainability is a robust public transportation system. These cities invest heavily in efficient, affordable, and widespread public transit networks, discouraging private vehicle use. Bicycle-friendly infrastructure, dedicated lanes, and bike-sharing programs promote a healthier and more sustainable mode of commuting.
3. Renewable Energy Integration:
The shift towards renewable energy is a defining characteristic of sustainable cities. Solar panels, wind turbines, and innovative technologies like smart grids are employed to harness clean energy. These cities set ambitious goals for carbon neutrality, relying on a blend of renewable sources to power their communities.
4. Social Inclusivity:
Sustainable cities prioritize social equity, ensuring that all residents have equal access to resources and opportunities. Affordable housing initiatives, mixed-use developments, and community spaces foster a sense of inclusivity. Social programs focus on education, healthcare, and cultural enrichment, creating a thriving and diverse urban landscape.
5. Environmental Conservation:
These cities go beyond the basics of waste management. They integrate green spaces within the urban fabric, establishing parks, urban forests, and protected natural areas. Water conservation measures, sustainable landscaping practices, and biodiversity preservation initiatives contribute to the overall environmental resilience of the city.
Copenhagen, Denmark: The Cycling Utopia

Pedaling Towards Progress:
Copenhagen, hailed as the cycling capital of the world, has seamlessly integrated biking into its urban lifestyle. The city’s commitment to cycling infrastructure extends beyond dedicated lanes; it includes bike-sharing programs, secure parking facilities, and even traffic signals designed with cyclists in mind. The result is not just reduced emissions but a healthier, more active populace.
Renewable Energy Leadership:
Copenhagen’s commitment to sustainability extends to its energy landscape. The city aims to be carbon-neutral by 2025, a lofty goal supported by wind turbines dotting its skyline and an ambitious plan for offshore wind farms. Harnessing wind power has become a symbol of Copenhagen’s dedication to clean energy solutions.
Singapore: The Garden City Reinvented
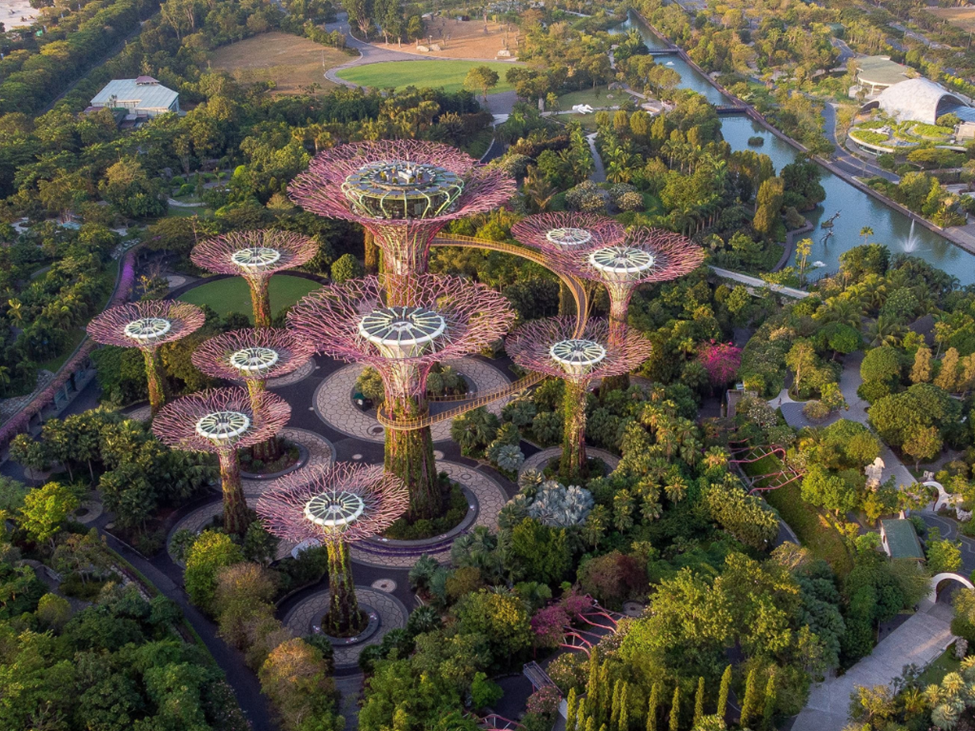

Urban Oasis Amidst Skyscrapers:
Singapore, often termed the Garden City, has taken green spaces to new heights—literally. Rooftop gardens, vertical greenery, and extensive parks weave seamlessly into the urban landscape. The commitment to maintaining a balance between concrete and greenery is not just aesthetically pleasing; it also contributes to improved air quality and biodiversity conservation.
Sustainable Architecture in the Skyline:
Singapore’s skyscrapers aren’t just marvels of engineering; they are exemplars of sustainable architecture. Buildings incorporate energy-efficient designs, green roofs, and smart technologies to minimize their environmental impact. The city’s skyline isn’t just a testament to economic prosperity but a symbol of a harmonious coexistence with nature.
Reykjavik, Iceland: Harnessing Nature’s Power
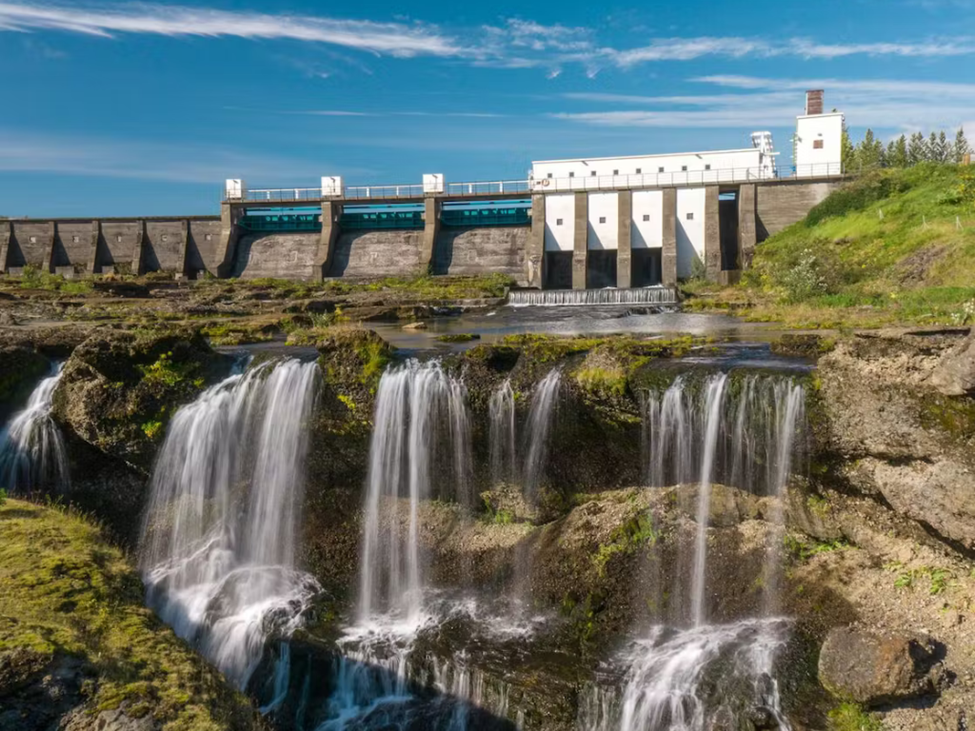

Geothermal Grandeur:
Situated in the land of fire and ice, Reykjavik taps into the geothermal energy beneath its surface. Utilizing the Earth’s natural heat for heating homes, powering industries, and generating electricity has not only reduced the city’s carbon footprint but also positioned it as a global leader in sustainable energy practices.
Compact Design for Efficiency:
Reykjavik’s compact urban design contributes to the city’s sustainability. Compact cities reduce the need for extensive transportation networks, promoting walkability and efficient public transit systems. This thoughtful urban planning minimizes energy consumption and enhances the overall quality of life for residents.
Vancouver, Canada: Where Nature and City Coexist

Embracing Nature Within the City:
Nestled between the Pacific Ocean and the mountains, Vancouver seamlessly integrates nature into its urban environment. The city prioritizes green initiatives, with an extensive network of parks, waterfronts, and green spaces. The commitment to preserving natural habitats within the city sets Vancouver apart as a model of sustainable urban planning.
Climate Leadership and Energy Efficiency:
Vancouver has set ambitious climate goals, aiming to become the world’s greenest city. The city’s efforts include stringent building codes promoting energy efficiency, a comprehensive public transit system, and initiatives to reduce carbon emissions. Vancouver’s commitment to sustainable practices extends to its vibrant cultural scene, emphasizing eco-friendly events and festivals.
Curitiba, Brazil: Pioneering Urban Sustainability

Revolutionizing Public Transportation:
Curitiba’s Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) system has become a global benchmark for sustainable urban transportation. The city prioritizes efficient and affordable public transit, reducing reliance on private vehicles. The BRT system, with dedicated lanes and strategically located stations, minimizes congestion and lowers carbon emissions, showcasing how innovative solutions can transform urban mobility.
Holistic Approach to Sustainability:
Curitiba’s sustainability journey extends beyond transportation. The city’s green spaces, waste recycling programs, and social housing initiatives exemplify a holistic approach to urban sustainability. Curitiba serves as a testament to how comprehensive planning can create a city that is not only environmentally conscious but also socially and economically resilient.
Room for Improvement: Elevating Sustainability to New Heights
While these cities shine as beacons of sustainability, there’s always room for improvement. Continuous innovation in renewable energy technologies, expansion of green infrastructure, and the development of circular economies are areas that demand attention. Collaborative efforts between government bodies, businesses, and residents are crucial to addressing emerging challenges and propelling these cities towards even greater heights of sustainability.
In conclusion, the top 5 sustainable cities invite us to dream of urban landscapes where nature and humanity coexist harmoniously. They are living proof that the pursuit of sustainability is not just a trend but a necessity. As these cities continue to evolve, they inspire others to follow suit, creating a global network of urban utopias committed to a greener and more sustainable future.
For more blogs please visit Envoybuzz